This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Local
1 - Neurodesk App

Determine System Privileges
Before running the app, check whether your system has privileged access (root/admin permissions). This determines which engine you need to use to run the app:
If you have privileged access → Use Docker or Podman Engine
If you do NOT have privileged access → Use TinyRange Engine, or run remote instance
Minimum System Requirements
- At least 5GB free space for neurodesktop base image.
- One of the following options, depending on system privileges:
With privileged access: Docker or Podman to run respective engines
Without privileged access: TinyRange Engine (included with Neurodesk App) and QEMU (only on macOS)
Downloading Neurodesk App
- Debian, Ubuntu Linux Installer x64
- Red Hat, Fedora, SUSE Linux Installer x64
- Debian, Ubuntu Linux Installer arm64
- Red Hat, Fedora, SUSE Linux Installer arm64
- Arch-based package via AUR
- macOS Intel Installer, macOS Apple silicon Installer
- Windows Installer
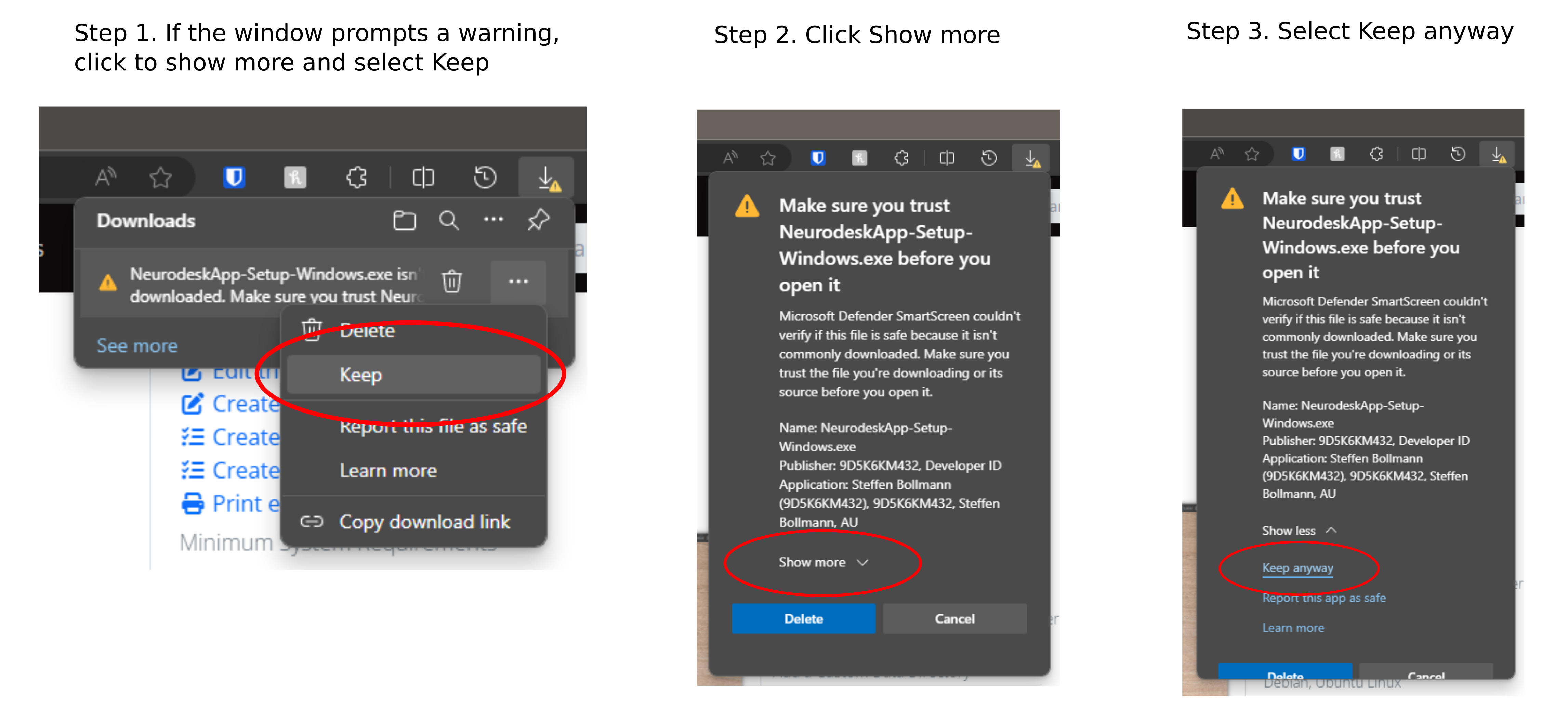
On Microsoft edge, follow these steps to download the executable file:
Installing Docker
If only connecting to a remote Neurodesk servers, you may skip Installing Docker
The Neurodesk App requires Docker to be installed on your computer. If you already have Docker installed, you can skip this step.
After installation, open a terminal (Linux/macOS) or command prompt (Windows) and run the following command to verify that Docker is working correctly:
docker --version
docker run hello-worldInstalling QEMU
The easist way to install QEMU on macOS is using Homebrew:
brew install qemuYou can verify the installation by running:
qemu-system-aarch64 --versionInstalling Neurodesk App
If you have an existing Neurodesk App installation, please first uninstall it by following the uninstall instructions here. Then, install the app for your system:
- Debian, Ubuntu Linux Installer:
sudo apt install -f ./NeurodeskApp-Setup-Debian.deb - Red Hat, Fedora, SUSE Linux Installer:
sudo rpm -i NeurodeskApp-Setup-Fedora.rpm - Arch-based package via AUR:
yay neurodesk(or follow instructions here) - macOS Installer: Double click the downloaded dmg file, then drag the NeurodeskApp.app to the Applications folder; for starting the app: Right click on the NeurodeskApp.app and select “Open”. For Apple Silicon systems (M1/M2): Make sure to enable Rosetta support in the docker settings for best performance!
- Windows Installer: Double click the downloaded exe file; Accept to install from an unknown publisher with Yes; then accept the license agreement and click finish at the end.
Launching Neurodesk App
The Neurodesk App can be launched directly from your operating system’s application menu, or by running the neurodeskapp command in the command line.
Note that the Neurodesk App will set the File Browser’s root directory based on the launch method used. The default working directory is the user’s home directory - this can be customized from the Settings dialog.
Sessions and Projects
Sessions represent local project launches and connections to existing Neurodesk servers. Each Neurodesk UI window in the app is associated with a separate session and sessions can be restored with the same configuration later on.
Session start options
You can start a new session by using the links at the Start section of the Welcome Page.
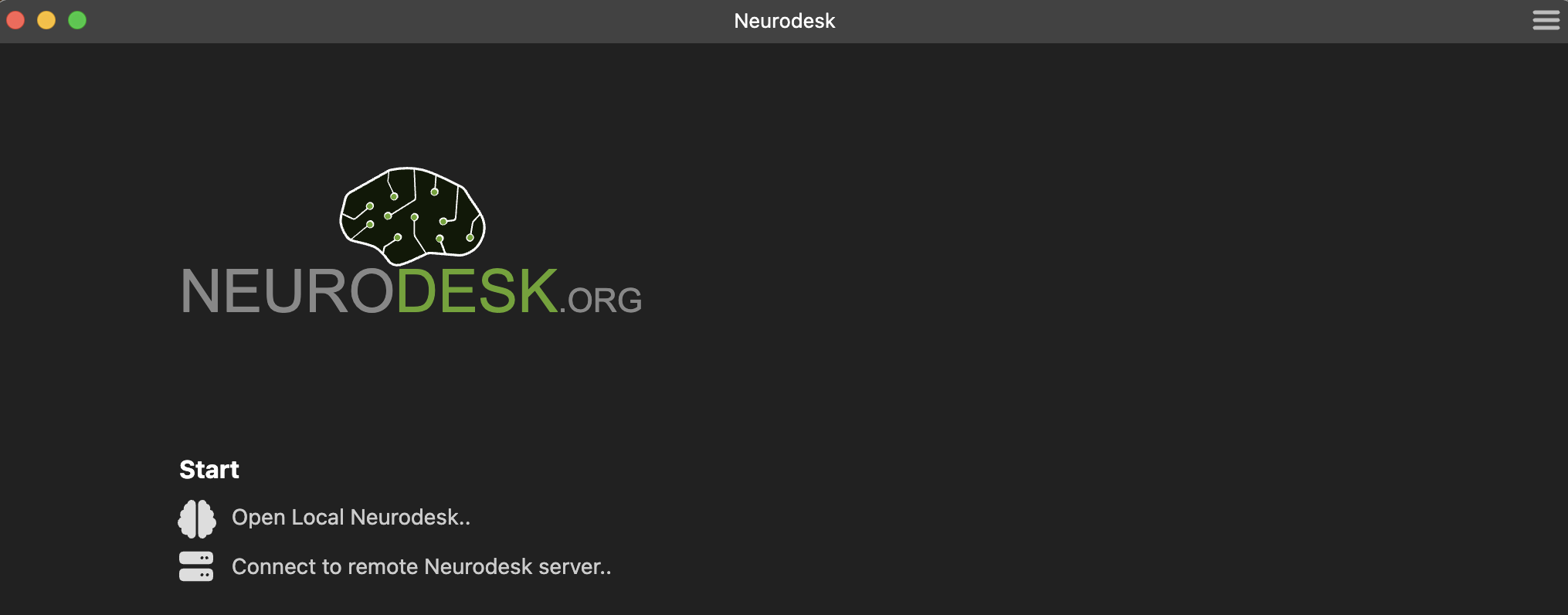
Open Local Neurodesk..creates a new session in the default working directory.Connect to remote Neurodesk server..creates a session by connecting to a remote Neurodesk server.
Previously opened sessions are stored as part of application data and they are listed on the Welcome Page. Clicking an item in the Recent sessions list restores the selected session.
Connecting to local Neurodesk
Neurodesk App creates new Neurodesk sessions by launching a locally running Neurodesk server and connecting to it. To open a local instance, click the Open Local Neurodesk.. button in the Start section of the Welcome Page.
This will show a Jupyterlab interface. There are two options to interact with Neurodesk through this interface:
- By clicking the
NeurodeskAppicon on the right. This will launch a new window to start a Neurodesk interface. - By module loading containers on the left bar. You can interact with loaded modules through the command line interface.

Connecting to a remote Neurodesk Server
It can also connect to an existing Neurodesk server instance that is running remotely. In order to connect to a server, click the Connect to remote Neurodesk server.. button in the Start section of the Welcome Page.

This will launch a dialog that automatically lists the remote Neurodesk server instances.
Select a server from the list or enter the URL of the Neurodesk application server. If the server requires a token for authentication, make sure to include it as a query parameter of the URL as well (/lab?token=<token-value>). After entering a URL hit Enter key to connect.
If the Persist session data option is checked, then the session information is stored and Neurodesk App will re-use this data on the next launch. If this option is not checked, the session data is automatically deleted at the next launch and servers requiring authentication will prompt for re-login.
You can delete the stored session data manually at any time by using the Clear History option in the Privacy tab of Settings dialog.

Configuration and data files
Neurodesk App stores data in ~/neurodesktop-storage for Linux and Mac, or C:/neurodesktop-storage for Windows, as default.
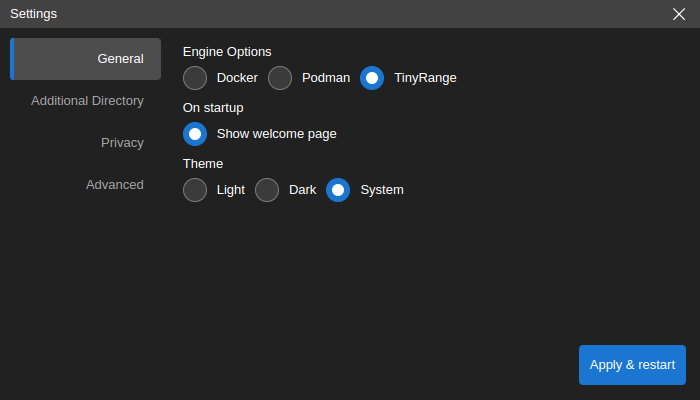
Add a Custom Data Directory
Neurodesk App stores its data in the following locations:
By default, /home/jovyan/neurodesktop-storage in the app (which is bound with local directory ~/neurodesktop-storage in Unix/MacOS or C:/neurodesktop-storage in Windows)
By choice, in the settings window below, select
Additional Directoryon the left side bar, clickChangebutton to select the local directory, then clickApply & restart. The next time you start the app, the data from the local directory can be found in /home/jovyan/data.
If you are using MacOS and Docker mounting an external hard drive will work out of the box. If you are using Podman you have to modify the Podman machine settings with the following commands once and then set the path in the Neurodesk App:
podman machine reset -f
podman machine init --rootful --now -v /Volumes:/Volumes -v $HOME:$HOME podman-machine-default
Troubleshooting Neurodesk App
/var/run/docker.sock: connect: permission denied, docker
This means that docker is not correctly setup yet, run:
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
sudo chown root:docker /var/run/docker.sock
sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sockFATAL:setuid_sandbox_host.cc(158)
If you see the error “FATAL:setuid_sandbox_host.cc(158)] The SUID sandbox helper binary was found, but is not configured correctly. Rather than run without sandboxing I’m aborting now. You need to make sure that /opt/NeurodeskApp/chrome-sandbox is owned by root and has mode 4755. Trace/breakpoint trap (core dumped)” this is caused by a recent change in Ubuntu 24.04.
A temporary workaround: Create the file /etc/apparmor.d/neurodeskapp With this content:
# This profile allows everything and only exists to give the
# application a name instead of having the label "unconfined"
abi <abi/4.0>,
include <tunables/global>
profile neurodeskapp "/opt/NeurodeskApp/neurodeskapp" flags=(unconfined) {
userns,
# Site-specific additions and overrides. See local/README for details.
include if exists <local/neurodeskapp>
}Then restart your computer. Then try to start the neurodesk app again.
Uninstalling Neurodesk App
Debian, Ubuntu Linux
sudo apt-get purge neurodeskapp # remove application
sudo rm /usr/bin/neurodeskapp # remove command symlink
rm -rf ~/.config/neurodeskapp # to remove application cacheRed Hat, Fedora, SUSE Linux
sudo rpm -e neurodeskapp # remove application
sudo rm /usr/bin/neurodeskapp # remove command symlink
rm -rf ~/.config/neurodeskapp # to remove application cacheArch-based Linux distributions
sudo pacman -Rs neurodeskapp-binmacOS
Find the application installation NeurodeskApp.app in Finder (in /Applications or ~/Applications) and move to Trash by using CMD + Delete. Clean other application generated files using:
rm -rf ~/Library/neurodeskapp # to remove application cache
rm -rf ~/Library/Application\ Support/neurodeskapp # to remove user dataWindows
On Windows, go to Windows Apps & Features dialog using Start Menu -> Settings -> Apps and uninstall Neurodesk App as shown below.
In order to remove application cache, delete C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\neurodeskapp directory. The AppData directory is a hidden directory - so make sure to activate hidden Items in the Windows explorer under View -> Show -> Hidden Items