Sherlock
Neurodesk runs on Stanfords supercomputer “Sherlock” and below are different ways of accessing it.
Using Neurodesk on Sherlock via ssh
Using Neurodesk containers
Setup your ~/.ssh/config
Host sherlock
ControlMaster auto
ForwardX11 yes
ControlPath ~/.ssh/%l%r@%h:%p
HostName login.sherlock.stanford.edu
User <sunetid>
ControlPersist yesand then connect to sherlock
ssh sherlockYou can module use the neurodesk modules (if they have been installed before - see instructions for installing and updating at the end of this page below):
module use $GROUP_HOME/modules
export APPTAINER_BINDPATH=/scratch,/tmpYou can also add these to your ~/.bashrc:
echo "module use $GROUP_HOME/modules/" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "export APPTAINER_BINDPATH=/scratch,/tmp" >> ~/.bashrcNow you can list all modules (Neurodesk modules are the first ones in the list):
ml avOr you can module load any tool you need:
ml fsl/6.0.7.18Submitting a job
put this in a file, e.g. submit.sbatch:
#!/bin/bash
#
#SBATCH --job-name=test
#SBATCH --time=01:00:00
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=2G
#SBATCH --output=logs/%x_%j.out
#SBATCH --error=logs/%x_%j.err
#SBATCH -p normal
module purge
module use $GROUP_HOME/modules/
module load ants/2.6.0
ants.... $1use sh_part to see which partitions and limits are available:
sh_partthen submit:
sbatch submit.sbatchto size jobs you can use ruse https://www.sherlock.stanford.edu/docs/user-guide/running-jobs/#sizing-a-job
module load system ruse
ruse ./myappor parallize across subjects:
for file in `ls sub*.nii`;
do echo "submitting job for $file";
sbatch submit.sbatch $file;
doneif you need lots of jobs, consider using array jobs: https://www.sherlock.stanford.edu/docs/advanced-topics/job-management/?h=array+jobs
starting a matlab job:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=invert
#SBATCH --time=00:03:00
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=3
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=4G
#SBATCH --output=logs/%x_%j.out
#SBATCH --error=logs/%x_%j.err
#SBATCH --partition=normal
#SBATCH --mail-type=ALL
module purge
module load matlab
matlab -batch matlab_file_without_the_dot_m_endingcheck:
squeue -u $USER
# or
squeue --me
# or to watch it continuesly:
watch -n 5 "squeue -u $USER"
# or get more details:
squeue --me -o "%.18i %.9P %.30j %.8u %.8T %.10M %.9l %.6D %.4C %.10m"
# or create an alias:
echo 'alias sq="squeue --me -o \"%.18i %.9P %.30j %.8u %.8T %.10M %.9l %.6D %.4C %.10m\""' >> ~/.bashrccancel jobs:
scancel <jobid>
scancel --name=my_job_namemore details https://www.sherlock.stanford.edu/docs/user-guide/running-jobs/#example-sbatch-script
Using GUI applications
First you need to connect to Sherlock with SSH forwarding (e.g. from a Linux machine or from your local neurodesk or from a mac with https://www.xquartz.org/ installed, or from windows using Mobaxterm)
and then request an interactive job and start the software:
sh_dev
ml mrtrix3
mrviewThis runs via x-forwarding and doesn’t work well, for a better experience see below how to start a full neurodesktop on Sherlock.
GPU support
request a GPU and then add –nv option:
sh_dev -g 1
module load fsl
export neurodesk_singularity_opts='--nv'
git clone https://github.com/neurolabusc/gpu_test.git
cd gpu_test/etest/
bash runme_gpu.shUsing Neurodesk on Sherlock via Ondemand
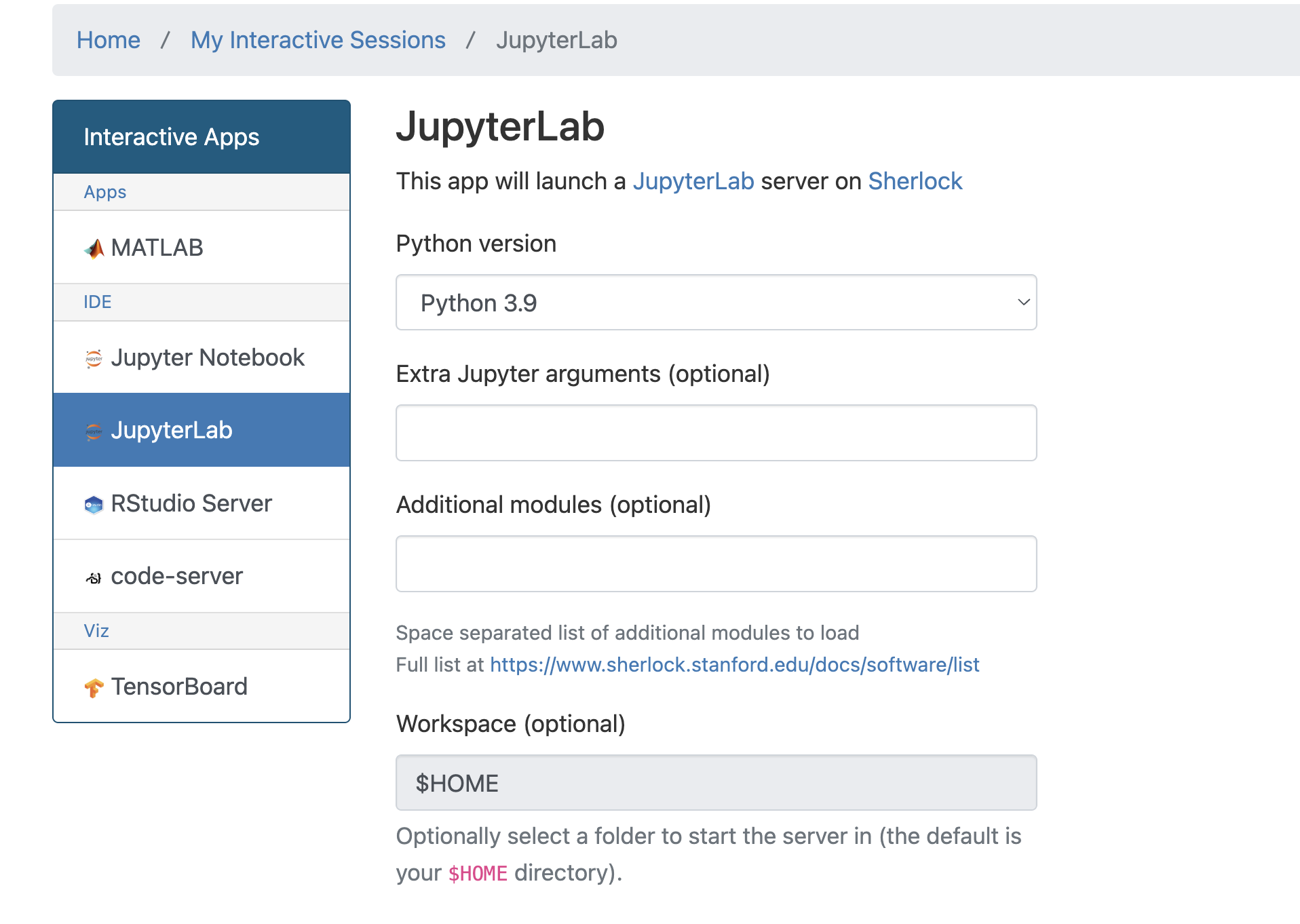
Open a jupyterlab session via Open On-Demand: https://ondemand.sherlock.stanford.edu/
Make sure to select python 3.9 - otherwise the HPC slurm plugin for jupyterlab will not work
Installing jupyterlab plugins
open a terminal in jupyterlab and install:
pip install jupyterlab_niivue ipyniivue jupyterlmod jupyterlab_slurmAfter the installation finished restart the jupyterlab session in Ondemand.
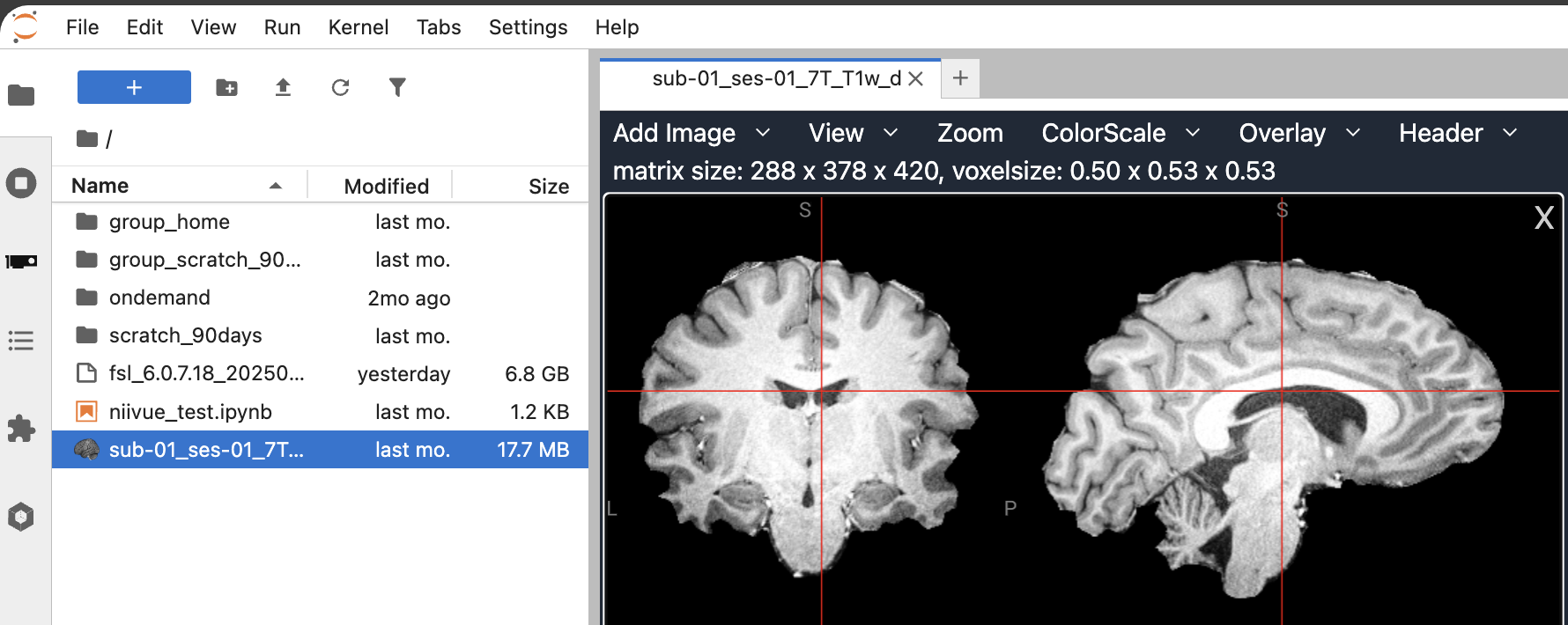
Neuroimaging Visualization in the File Browser and notebooks of Jupyter Lab
The pip install jupyterlab_niivue added an extension to jupyterlab that visualizes neuroimaging data directly via a double-click in the filebrowser in jupyterlab:
Using containers inside a jupyter notebook
The install of pip install jupyterlmod made the following possible inside a jupyter notebook:
import os
import lmod
group_home = os.environ.get("GROUP_HOME", "")
os.environ["MODULEPATH"] = os.path.abspath(f"{group_home}/neurodesk/local/containers/modules/")
await lmod.load('fsl')now you can run command line tools in a notebook
!betUsing niivue inside a jupyter notebook
The install of pip install ipyniivue allows interactive visualizations inside jupyter notebooks: See examples here https://niivue.github.io/ipyniivue/gallery/index.html
e.g.:
from ipyniivue import NiiVue
nv = NiiVue()
nv.load_volumes([{'path': 'sub-01_ses-01_7T_T1w_defaced_brain.nii.gz'}])
nvChecking on SLURM inside jupyter lab
The install of pip install jupyterlab_slurm added a plugin that allows monitoring slurm jobs.
Using Neurodesk via a full neurodesktop session
This is an ideal setup for visualizing results on Sherlock and for running GUI applications. You need to run these commands on your computer (e.g. MacOS/Linux/Windows WSL2):
downloading startup script
curl -J -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/neurodesk/neurodesk.github.io/refs/heads/main/content/en/Getting-Started/Installations/connectSherlock.shstarting session
bash connectSherlock.shAlternative to running connectSherlock.sh: start neurodesktop manually when already inside a job on sherlock
apptainer run \
--fakeroot \
--nv \
--overlay $SCRATCH/neurodesktop-overlay.img \
--bind $GROUP_HOME/neurodesk/local/containers/:/neurodesktop-storage/containers \
--no-home \
--env CVMFS_DISABLE=true \
--env NB_UID=$(id -u) \
--env NB_GID=$(id -g) \
--env NEURODESKTOP_VERSION=latest \
$GROUP_HOME/neurodesk/neurodesktop-neurodesktop_latest.sif \
start-notebook.py --allow-rootconnecting with VScode
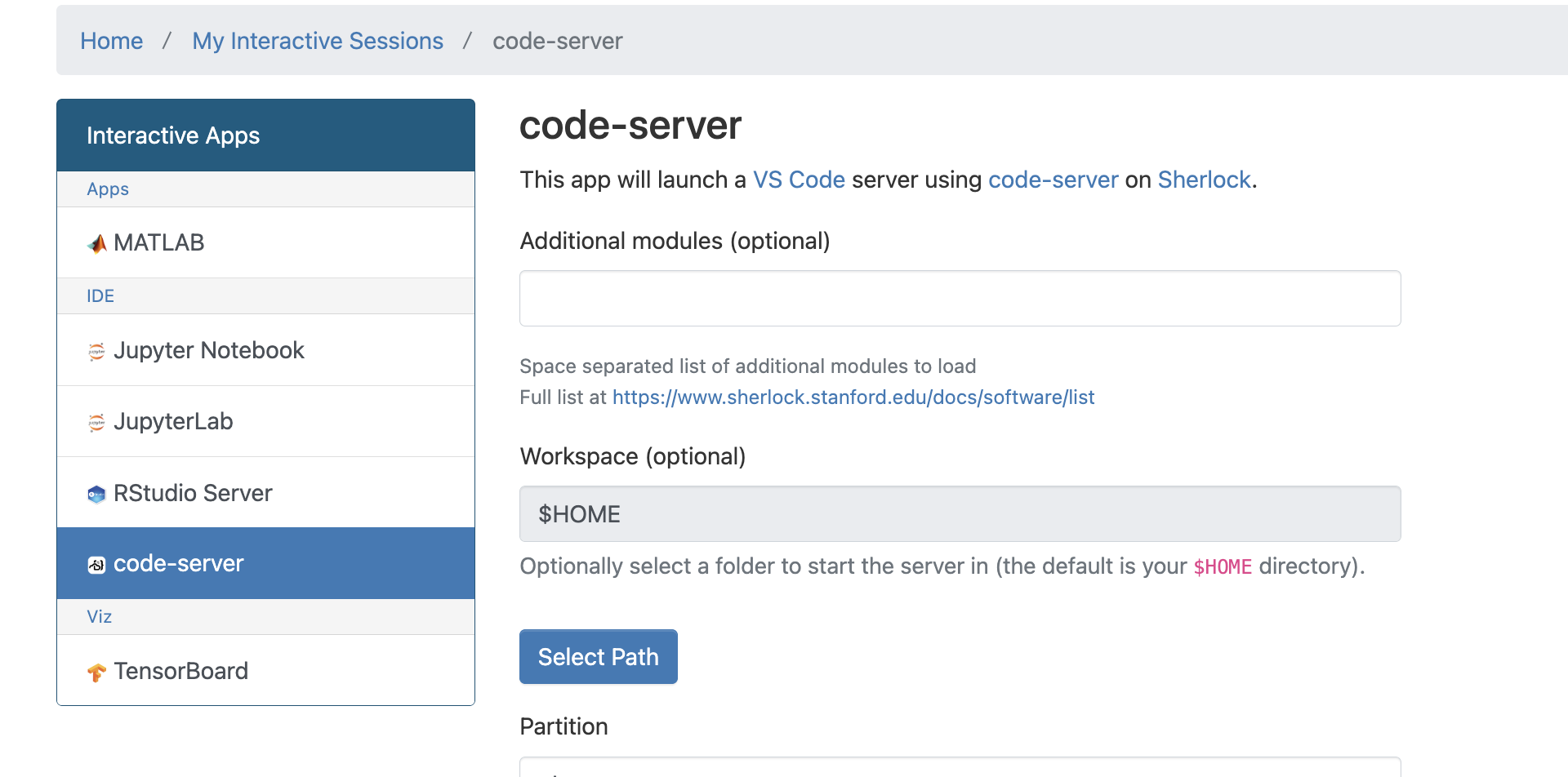
VScode server does not work on he login nodes due to resource restrictions. It might be possible to run it inside a compute job and inside a container. However, it is possible to run vscode server through ondemand:
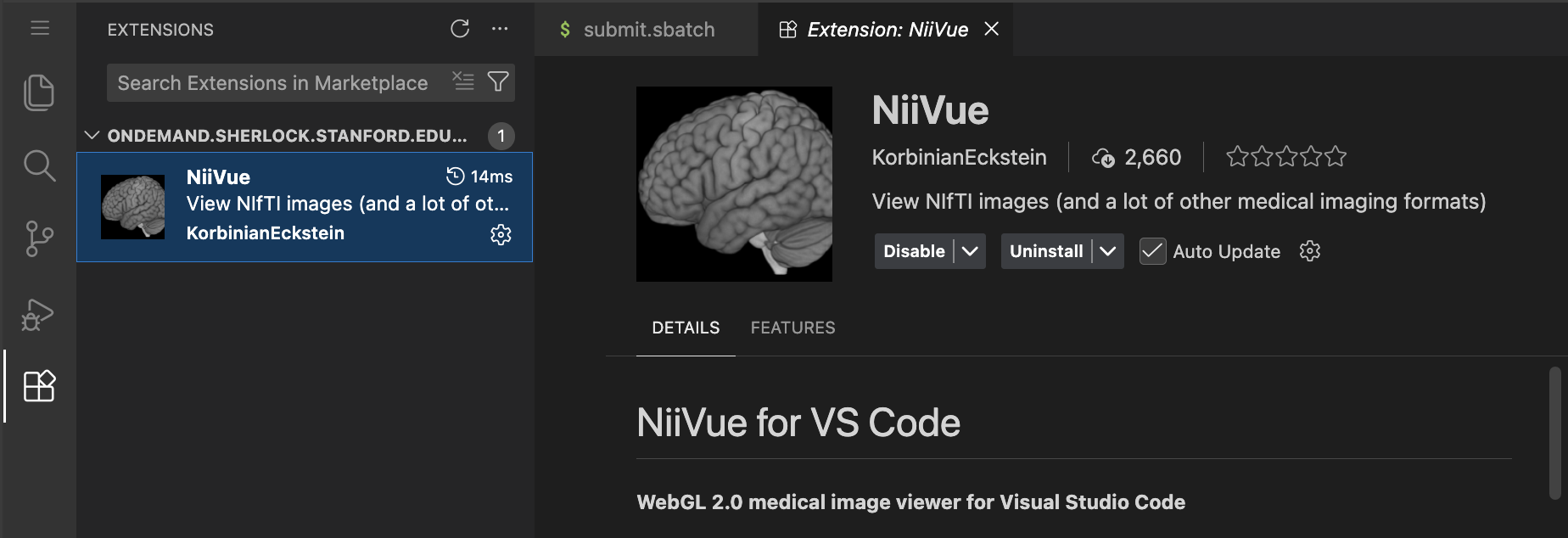
A great extension to install is niivue for vscode which allows visualizing neuroimaging data in vscode:
and for AI coding:
- claude code
- gemini CLI companion
- gemini code assist
and for checking on slurm jobs in vscode:
- slurm–
and for matlab scripts:
- MATLAB Extension for Windsurf – path is: /share/software/user/restricted/matlab/R2022b/
useful shortcuts:
- you can execute a line from your scripts on the terminal via setting a keyboard shortcut to “Terminal: Run Selected Text in Active Terminal” - that makes testing scripts and debugging them quite quick
connecting with Cursor
Cursor does not work on the login nodes due to resource restrictions. It might be possible to run it inside a compute job and inside a container.
using coding agents on sherlock
Copilot CLI — an extension of GitHub Copilot that answers natural-language prompts and generates shell commands and code snippets interactively in the CLI. Integrates with developer workflow and git metadata, good at scaffolding repo-level changes. Use this for drafting Slurm scripts, shell-based data-movement commands, Makefiles, container entrypoints, and succinct code edits from the terminal. Caution: always validate generated shell commands before running on Oak.
ml copilot-cli
copilotGemini CLI — a CLI assistant that can generate code from Google’s Gemini family of models (via Google Cloud/Vertex AI or client tooling). Provides strong multilingual reasoning and contextual code completion. Use this for translating research intent into cloud and hybrid workflows, generating code for TPU/GPU workloads, and producing infrastructure-as-code snippets that tie to GCP resources. Caution: always confirm data residency and compliance requirements for sensitive data.
ml gemini-cli
geminiClaude Code (Claude family) — a coding-specialized variant in the Anthropic Claude model family aimed at code generation, refactoring, and reasoning tasks. Provides conversational reasoning about code, multi-step planning for algorithmic tasks, and safer-response tuning relative to generic models. Caution: check private endpoints/dedicated instances before sending sensitive datasets.
ml claude-code
claudeCodex — an OpenAI model family good at producing short code snippets, language translations, and API glue, historically the basis for many coding assistants. Use this for scaffold code, translating pseudocode to working scripts, and generating wrappers for system calls and schedulers. Caution: watch out for API hallucinations and insecure shell usage suggestions; verification in GPT-4 (which often supersedes Codex in capability and safety) advised.
ml codex
codexCrush CLI — an all-around CLI assistant from the Charmbracelet Go-based “ecosystem” intended to improve interactive developer workflows and scripting. Use it for interactive shells or task runners, pipeline composition for local data preprocessing, productivity (nicer prompts, piping primitives, nicer output formatting), or small automation tasks such as repo tooling and glue scripts.
ml crush
crushMisc
note on miniconda
we need an older version of Miniconda on Sherlock due to the outdated glibc:
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-py310_23.3.1-0-Linux-x86_64.sh
bash Miniconda3-py310_23.3.1-0-Linux-x86_64.shnote on MRIQC
NOTE: MRIQC has its $HOME variable hardcoded to be /home/mriqc. This leads to problems. A workaround is to run this before mriqc:
export neurodesk_singularity_opts="--home $HOME:/home"note on AFNI
NOTE: If you are using AFNI then the default detach behavior will cause SIGBUS errors and a crash. To fix this run AFNI with:
afni -no_detachData transfer
Transfer files to and from Onedrive
First install rclone on your computer and set it up for onedrive. Then copy the config file ~/.config/rclone/rclone.conf to sherlock. Then run rclone on sherlock:
ml system
ml rclone
rclone ls
rclone copysetting up rclone for onedrive (needs to be done on a computer with a browser, so not sherlock):
rclone config
# select n for new remote
# enter a name, e.g. onedrive
# select one drive from the list, depending on the rclone version this could be 38
# hit enter for default client_id
# hit enter for default client_secret
# select region 1 Microsoft Global
# hit enter for default tenant
# enter n to skip advanced config
# enter y to open a webbrowser and authenticate with onedrive
# enter 1 for config type OneDrive Personal or Business
# hit enter for default config_driveid
# enter y to accept
# enter y again to confirm
# then quit config q
# now test:
rclone ls onedrive:
# if it's not showing the files from your onedrive, change the config_driveid in ~/.config/rclone/rclone.conf
vi ~/.config/rclone/rclone.confmounting sherlock files on your computer through sshfs
install sshfs for your operating system, e.g. on MacOS:
brew tap macos-fuse-t/homebrew-cask
brew install fuse-t-sshfsthen mount for macos:
mkdir ~/sherlock_scratch
sshfs sciget@dtn.sherlock.stanford.edu:./ ~/sherlock_scratch -o subtype=fuse-ton linux:
mkdir ~/sherlock_scratch
sshfs <sunetid>@dtn.sherlock.stanford.edu:./ ~/sherlock_scratchTransfer files using datalad
ml contribs
ml poldrack
ml datalad-uv
dataladTransfer files via scp
# this will transfer a file from your computer to your scratch space
scp foo <sunetid>@dtn.sherlock.stanford.edu:
# this will transfer a directory from sherlock to your computer:
scp -r <sunetid>@dtn.sherlock.stanford.edu:/scratch/groups/<your_group_here>/<your_directory_here> .Managing Neurodesk on Sherlock
Installing Neurodesk for a lab
This is already done and doesn’t need to be run again!
cd $GROUP_HOME/
git clone https://github.com/neurodesk/neurocommand.git neurodesk
cd neurodesk
pip3 install -r neurodesk/requirements.txt --user
bash build.sh --cli
bash containers.sh
export APPTAINER_BINDPATH=`pwd -P`Installing additional containers
Everyone has write permissions and can download and install new containers.
cd $GROUP_HOME/neurodesk
git pull
bash build.sh
bash containers.sh
# to search for a container:
bash containers.sh freesurfer
# then install the choosen version by copy and pasting the specific command install command displayedIf a new container was installed from Neurodesktop, the paths will need to be adjusted to work outside of Neurodesktop for the rest of sherlock:
sh_dev
#First, test if that happened:
cd $GROUP_HOME/neurodesk/local/containers/
find . -maxdepth 2 -type f -exec grep -l '/home/jovyan/' {} \; 2>/dev/null
cd $GROUP_HOME/neurodesk/local/containers/modules
find . -maxdepth 2 -type f -exec grep -l '/home/jovyan/' {} \; 2>/dev/null
#Then fix for modules:
cd $GROUP_HOME/neurodesk/local/containers/modules
find . -maxdepth 2 -type f -exec sh -c 'if grep -q "/home/jovyan/neurodesktop-storage/containers/" "$1"; then sed -i "s|/home/jovyan/neurodesktop-storage/containers/|${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/local/containers/|g" "$1" && echo "Updated: $1"; fi' sh {} \;
#Then fix for containers:
cd $GROUP_HOME/neurodesk/local/containers
find . -maxdepth 2 -type f -exec sh -c 'if grep -q "/home/jovyan/neurodesktop-storage/containers/" "$1"; then sed -i "s|/home/jovyan/neurodesktop-storage/containers/|${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/local/containers/|g" "$1" && echo "Updated: $1"; fi' sh {} \;Updating Neurodesktop image
ssh sherlock
sh_dev -m 32 -p normal -c 4
export VERSION="2026-01-30"
cd ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk
export APPTAINER_TMPDIR=$SCRATCH/apptainer_temp
mkdir -p $APPTAINER_TMPDIR
apptainer pull docker://ghcr.io/neurodesk/neurodesktop/neurodesktop:${VERSION}
rm ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/neurodesktop_latest.sif
ln -s ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/neurodesktop_${VERSION}.sif ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/neurodesktop_latest.sif Or submit the update as a single Slurm job:
sbatch -p normal -c 4 --mem=32G --job-name=neurodesktop-update --wrap 'export VERSION="2026-01-30"; cd ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk; export APPTAINER_TMPDIR=$SCRATCH/apptainer_temp; mkdir -p $APPTAINER_TMPDIR; apptainer pull docker://ghcr.io/neurodesk/neurodesktop/neurodesktop:${VERSION}; rm ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/neurodesktop_latest.sif; ln -s ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/neurodesktop_${VERSION}.sif ${GROUP_HOME}/neurodesk/neurodesktop_latest.sif'